(duplicate of this StackOverflow answer)
Start a new project
- In a new folder, type
npm initto start a new project. - Make sure to use a Node >= v14 (I use Node v18 – and Volta can be useful to manage several versions of Node for Windows)
- Install some dependencies:
npm install axios @azure/msal-node uuid
Certificate
In the past, we could use the add-in application feature to get a token, but Microsoft announced it will be retired.
We now need to pass through an Azure application to get it. But before creating the Azure app, we need to create a Private Certificate key.
- Create the file
Create-SelfSignedCertificate.ps1using the below code (source):
#Requires -RunAsAdministrator
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Creates a Self Signed Certificate for use in server to server authentication
.DESCRIPTION
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/solution-guidance/security-apponly-azuread#setting-up-an-azure-ad-app-for-app-only-access
.EXAMPLE
.\Create-SelfSignedCertificate.ps1 -CommonName "MyCert" -StartDate 2015-11-21 -EndDate 2017-11-21
This will create a new self signed certificate with the common name "CN=MyCert". During creation you will be asked to provide a password to protect the private key.
.EXAMPLE
.\Create-SelfSignedCertificate.ps1 -CommonName "MyCert" -StartDate 2015-11-21 -EndDate 2017-11-21 -Password (ConvertTo-SecureString -String "MyPassword" -AsPlainText -Force)
This will create a new self signed certificate with the common name "CN=MyCert". The password as specified in the Password parameter will be used to protect the private key
.EXAMPLE
.\Create-SelfSignedCertificate.ps1 -CommonName "MyCert" -StartDate 2015-11-21 -EndDate 2017-11-21 -Force
This will create a new self signed certificate with the common name "CN=MyCert". During creation you will be asked to provide a password to protect the private key. If there is already a certificate with the common name you specified, it will be removed first.
#>
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$CommonName,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[DateTime]$StartDate,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[DateTime]$EndDate,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false, HelpMessage="Will overwrite existing certificates")]
[Switch]$Force,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[SecureString]$Password
)
# DO NOT MODIFY BELOW
function CreateSelfSignedCertificate(){
#Remove and existing certificates with the same common name from personal and root stores
#Need to be very wary of this as could break something
if($CommonName.ToLower().StartsWith("cn="))
{
# Remove CN from common name
$CommonName = $CommonName.Substring(3)
}
$certs = Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\my | Where-Object{$_.Subject -eq "CN=$CommonName"}
if($certs -ne $null -and $certs.Length -gt 0)
{
if($Force)
{
foreach($c in $certs)
{
remove-item $c.PSPath
}
} else {
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Red "One or more certificates with the same common name (CN=$CommonName) are already located in the local certificate store. Use -Force to remove them";
return $false
}
}
$name = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CX500DistinguishedName.1"
$name.Encode("CN=$CommonName", 0)
$key = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CX509PrivateKey.1"
$key.ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider"
$key.KeySpec = 1
$key.Length = 2048
$key.SecurityDescriptor = "D:PAI(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;SY)(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;BA)(A;;0x80120089;;;NS)"
$key.MachineContext = 1
$key.ExportPolicy = 1 # This is required to allow the private key to be exported
$key.Create()
$serverauthoid = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CObjectId.1"
$serverauthoid.InitializeFromValue("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") # Server Authentication
$ekuoids = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CObjectIds.1"
$ekuoids.add($serverauthoid)
$ekuext = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionEnhancedKeyUsage.1"
$ekuext.InitializeEncode($ekuoids)
$cert = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CX509CertificateRequestCertificate.1"
$cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey(2, $key, "")
$cert.Subject = $name
$cert.Issuer = $cert.Subject
$cert.NotBefore = $StartDate
$cert.NotAfter = $EndDate
$cert.X509Extensions.Add($ekuext)
$cert.Encode()
$enrollment = new-object -com "X509Enrollment.CX509Enrollment.1"
$enrollment.InitializeFromRequest($cert)
$certdata = $enrollment.CreateRequest(0)
$enrollment.InstallResponse(2, $certdata, 0, "")
return $true
}
function ExportPFXFile()
{
if($CommonName.ToLower().StartsWith("cn="))
{
# Remove CN from common name
$CommonName = $CommonName.Substring(3)
}
if($Password -eq $null)
{
$Password = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter Password to protect private key" -AsSecureString
}
$cert = Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\my | where-object{$_.Subject -eq "CN=$CommonName"}
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $cert -Password $Password -FilePath "$($CommonName).pfx"
Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -Type CERT -FilePath "$CommonName.cer"
}
function RemoveCertsFromStore()
{
# Once the certificates have been been exported we can safely remove them from the store
if($CommonName.ToLower().StartsWith("cn="))
{
# Remove CN from common name
$CommonName = $CommonName.Substring(3)
}
$certs = Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\my | Where-Object{$_.Subject -eq "CN=$CommonName"}
foreach($c in $certs)
{
remove-item $c.PSPath
}
}
if(CreateSelfSignedCertificate)
{
ExportPFXFile
RemoveCertsFromStore
}
- Open a PowerShell console as an administrator
- Create the certificate with a command like
.\Create-SelfSignedCertificate.ps1 -CommonName "SharePointOnlinePrivateKey" -StartDate 2024-04-01 -EndDate 2035-01-01(if you receive an error, make sure to allow running this kind of script with the commandSet-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned) - A password is required (e.g. "HereIsMyPass1223")
- Two files are created:
SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pfxandSharePointOnlinePrivateKey.cer
We're going to install OpenSSL to convert the pfx file to a pem:
- Install OpenSSL (e.g. the light version for Win64) as an administrator
- Find the OpenSSL installation directory (e.g.
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\) - Open the
start.batfile from this OpenSSL directory - A command window opens – go to the directory where the
SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pfxfile is (e.g.cd C:\Users\Aymeric\Documents\nodejs\spo-experiments) - In the OpenSSL command window, type
openssl pkcs12 -in SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pfx -out SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pem(the password entered in the previous steps will be asked three times)
We should now have a file called SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pem
Azure Application
It's time to create the related Azure application:
- Go to https://portal.azure.com
- Go to the Microsoft Entra ID section
- Go to the "App Registrations", and click on "New registration"
- I won't detail all the steps to create the app
- Give a name to the app (e.g. "SharePoint Online Remote Access")
Get Thumbprint
We need the thumbprint:
- Go to "Certificates & secrets" section
- Go to "Certificates" tab (see how) and upload the
SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.cerfile you created before - Once uploaded, it will provide "Thumbprint" (e.g. "F7D8D4F2F140E79B215899BD93A14D0790947789") – copy this value for a later use.
Get Client Id and Tenant Id
We need the clientId and the tenantId:
- From the overview page of your app, copy the "Application (client) Id" (e.g. "75284292-7515-4e2f-aae9-d1777527dd7b") and the "Directory (tenant) ID" (e.g. "945c177a-83a2-4e80-9f8c-5a91be5752dd")
Platform configuration
Additional configuration required for the application:
- Go to "Authentication" menu, and under "Platform configurations", click on "Add a Platform"
- Choose "Web" and enter
https://localhostfor "Redirect URLs" - Choose "Access Token" and "ID Token" in the "Implicit grant and hybrid flows" section
API Permissions
We want to give the permissions to the Azure app to get access to only one (or more) specific Sites Collection, but not all of the tenant site collections. To do so, we only need the Sites.Selected permissions (ref1 and ref2).
First, let's select it from a Microsoft Graph perspective:
- Go to the "API Permissions" section from the left navigation
- Click on "Add a permission"
- Select "Microsoft Graph"
- Then "Application Permissions"
- Select "Sites.Selected"
Then, let's select it for SharePoint Online REST perspective:
- From the same section, select "SharePoint"
- Then "Application Permissions"
- Select "Sites.Selected"

Remark: you might need to contact the IT team to get your API Permissions approved/granted.
Get Client Secret
We need the clientSecret:
- Go to the "Certificates and Secrets" section from the left navigation
- Go to "Client Secret" and click on "New client secret"
- In "Description" you can put something like "SharePoint Online Remote Access", and choose 365 days for the expiration
- Once done, make sure to copy
Value(e.g. "rVE7Q~Z1BhRXaljbj7SPg~U2HYJRR-feckrxKbCt") that is ourclientSecret
App permissions on Site Collection
It's time to indicate that the Azure application can have access to a specific Site Collection (e.g. https://mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso).
To proceed, we need the siteId:
- Go to the SharePoint website (e.g. https://mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso)
- Click right in the page to see the source (or
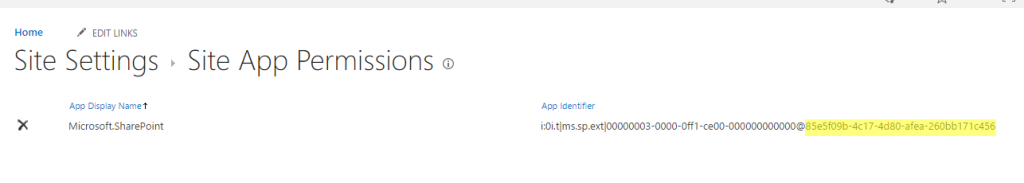
CTRL U) - Search for the variable
siteId(e.g. "7d6d9e18-e8de-4b7c-9582-3f978726f356")
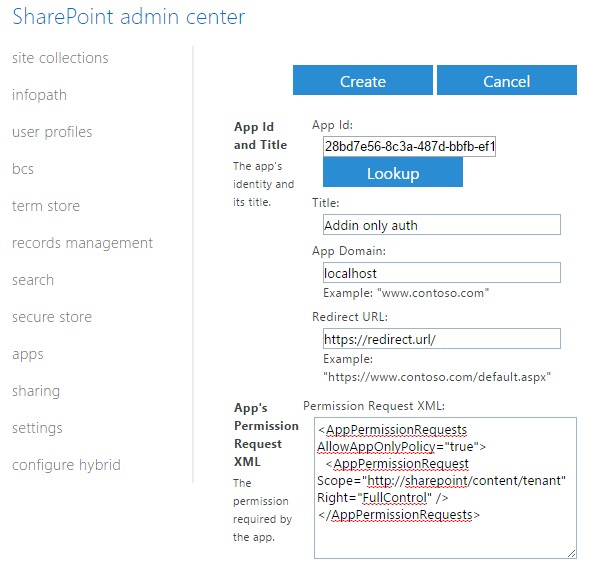
To give the permissions to the app, a special command must be entered (see this video for more information). In theory, the site collection admin can do it, but it might be restricted in your organization, and you'll need the assistance of a tenant admin.
We need the AppId (as known as clientId) and DisplayName (as known as the Azure app name):
$targetSiteUri = 'https://mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso' Connect-PnpOnline $targetSiteUri Grant-PnPAzureADAppSitePermission -AppId '75284292-7515-4e2f-aae9-d1777527dd7b' -DisplayName 'SharePoint Online Remote Access' -Site $targetSiteUri -Permissions Write
Interact with SharePoint
Microsoft Graph only needs a client_secret, while SharePoint REST API needs a client_assertion from the Certificate Private key.
So, let's start with Microsoft Graph to verify our Azure app has the correct access permissions.
Microsoft Graph
Below is the script we can use:
const axios = require('axios');
// our constants that we found previously
// they should not be hard-coded in your script, but store in a safe place
const tenantId = '945c177a-83a2-4e80-9f8c-5a91be5752dd';
const clientId = '75284292-7515-4e2f-aae9-d1777527dd7b';
const clientSecret = 'rVE7Q~Z1BhRXaljbj7SPg~U2HYJRR-feckrxKbCt';
const siteId = '7d6d9e18-e8de-4b7c-9582-3f978726f356';
async function getAccessToken() {
const resource = 'https://graph.microsoft.com';
try {
const response = await axios.post(`https://login.microsoftonline.com/${tenantId}/oauth2/v2.0/token`, new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: 'client_credentials',
client_id: clientId,
client_secret: clientSecret,
scope: `${resource}/.default`
}), {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
});
return response.data.access_token;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error getting access token:', error);
throw error;
}
}
// get a SharePoint item using Graph
getAccessToken()
.then(token => {
// we need to find the siteId for each level
// we could use `https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites/${siteId}/sites` to find the children sites Id
// mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso/Toolbox -> 919f3ff8-2cfd-469d-ac2c-cf58475ee72a
// mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso/Toolbox/Demo -> 37af7205-ebd1-49e5-a770-cdb182d2ae81
return axios.get(`https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites/${siteId}/sites/919f3ff8-2cfd-469d-ac2c-cf58475ee72a/sites/37af7205-ebd1-49e5-a770-cdb182d2ae81/lists/Assets/items/123?expand=fields(select=Title)`, {
headers:{
'Authorization':'Bearer '+token,
'Accept': 'application/json'
}
})
})
.then(res => {
console.log(res.data);
})
.catch(err => {
console.log("err => ", err.response.data)
})
SharePoint Online REST API
If it worked with the Graph version, it means we can now test with the SharePoint REST API:
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require("fs");
const crypto = require("crypto");
const msal = require("@azure/msal-node");
const { v4: uuid } = require('uuid');
// our constants that we found previously
// they should not be hard-coded in your script, but store in a safe place
const tenantId = '945c177a-83a2-4e80-9f8c-5a91be5752dd';
const clientId = '75284292-7515-4e2f-aae9-d1777527dd7b';
const clientSecret = 'rVE7Q~Z1BhRXaljbj7SPg~U2HYJRR-feckrxKbCt';
const resource = 'https://mycompany.sharepoint.com';
const privateKeyPassPhrase = "HereIsMyPass1223";
const thumbprint = "F7D8D4F2F140E79B215899BD93A14D0790947789";
// generate the client_assertion
function getClientAssertion () {
// source: https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-js/blob/dev/lib/msal-node/docs/certificate-credentials.md
// decrypt the private key
const privateKeySource = fs.readFileSync("./SharePointOnlinePrivateKey.pem");
const privateKeyObject = crypto.createPrivateKey({
key: privateKeySource,
passphrase: privateKeyPassPhrase,
format: "pem",
});
const privateKey = privateKeyObject.export({
format: "pem",
type: "pkcs8",
});
const config = {
auth: {
clientId: clientId,
authority: `https://login.microsoftonline.com/${tenantId}`,
clientCertificate: {
thumbprint: thumbprint, // a 40-digit hexadecimal string
privateKey: privateKey,
},
},
};
// Create msal application object
const cca = new msal.ConfidentialClientApplication(config);
const helper = {
createNewGuid:uuid
}
const issuer = clientId;
const jwtAudience = `https://login.microsoftonline.com/${tenantId}/oauth2/v2.0/token`;
return cca.clientAssertion.getJwt(helper, issuer, jwtAudience);
}
async function getAccessToken() {
// see https://github.com/SharePoint/sp-dev-docs/issues/5889 and https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity-platform/v2-oauth2-client-creds-grant-flow#second-case-access-token-request-with-a-certificate
try {
const response = await axios.post(`https://login.microsoftonline.com/${tenantId}/oauth2/v2.0/token`, new URLSearchParams({
client_id: clientId,
scope: `${resource}/.default`,
client_assertion_type: "urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer",
client_assertion: getClientAssertion(),
grant_type: 'client_credentials',
}), {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
});
return response.data.access_token;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error getting access token:', error);
throw error;
}
}
// run the script
getAccessToken()
.then(token => {
return axios.get(`https://mycompany.sharepoint.com/sites/contoso/Toolbox/Demo/_api/web/lists/getbytitle('Assets')/items(123)?$select=Title`, {
headers:{
'Authorization':'Bearer '+token,
'Accept': 'application/json; odata=verbose'
}
})
})
.then(response => {
console.log(response.data)
})
.catch(console.log)